Categories
Archives

Media consultant and IPTC Individual Member Denise Durand Kremer gave a presentation on IPTC Photo Metadata at the Seminário Fototeca Brasileira – the Brazilian Photo Library Seminar.
Over three days, more than 80 people got together to discuss the idea of a national photo library for Brazil. Denise was invited by the Collection and Market group Acervo e Mercado to talk about her experience as an iconographic researcher and about the IPTC standard for photographic metadata.
Photographers, teachers, researchers, archivists and public managers from institutions such as the Museu da Imagem e do Som de São Paulo – MIS (Museum of Image and Sound of São Paulo), Funarte, Instituto Moreira Salles, Zumví and Arquivo Afro Fotográfico participated in the event.
The meeting ended with a commitment from the Executive Secretary of the Ministry of Culture, to set up a working group to take the idea forward.
The seminar was recorded and will be available on SescTV.
Update, 6 August 2024: The video has now been released publicly. You can view Denise’s section below (in Brazilian Portuguese):
Thanks very much Denise for spreading the word about IPTC standards in Brazil!

Last week CEPIC, the “centre of the picture industry”, held its annual Congress in Juan-les-Pins in France. This was the second time that the event was held at the Palais du Congres in Juan-les-Pins near Antibes, which is proving to be a great venue for the Congress with many repeat visitors who also attended last year.
IPTC was well represented at the event, with Managing Director Brendan Quinn presenting on two panels and many other IPTC members involved in presentations, panels or simply attending the event. IPTC members either presenting or in attendance included Google, Shutterstock, Getty Images, ANSA, IMATAG, PA Media / Alamy, TT, dpa, Adobe, Xinhua, Activo, APA, European Pressphoto Agency EPA and possibly more that we have missed!

One of the highlights for us was the Provenance and AI panel moderated by Anna Dickson, who until recently was with Google but is now with another IPTC member, Shutterstock. Presenters on this panel included Katharina Familia Almonte, product manager at Google, Andy Parsons, Director of the Content Authenticity Initiative (although Brendan ended up presenting his slides due to it being 4.30am for Andy in New York at the time!); Mathieu Desoubeaux, CEO of IPTC startup member IMATAG, and Brendan Quinn, Managing Director of IPTC.
Brendan used the opportunity to introduce the IPTC Media Provenance Committee and the work that the IPTC is doing on creating a C2PA Trust List for media organisations. Brendan put out a call for other media organisations who may be interested in joining the next cohort of certificate holders who will be able to obtain a certificate stored on the trust list and use it to cryptographically sign their media content. The discussion went on to look at the issues around using both C2PA and watermarking technology to protect image content.
Later in the day was the panel “Where Law and Technology Meet.” Moderated by Lars Modie (CEPIC, previously of IBL Bildbyrå / TT in Swededn) with speakers: Serguei Fomin (IQPlug, IPTC CEPIC representative), Brendan Quinn (IPTC), Franck Bardol (University of Geneva), Nancy Wolff (partner at the intellectual property, media and entertainment law firm of Cowan, DeBaets, Abrahams & Sheppard, LLP and DMLA counsel) and Katherine Briggs of Australian agency Envato which was recently acquired by Shutterstock.

At this panel, Brendan outlined IPTC’s recent guidance on metadata for generative AI images. This includes the Digital Source Type property but also guidance on using the Creator, Contributor, and Data Mining properties to signal ownership and rights licensing information associated with images, particularly for engines that “scrape” web content to train generative AI models.
Many stimulating conversations always make the CEPIC Congress a valuable event for us to attend, and we are already looking forward to next year’s instalment.

Last week, the IPTC Spring Meeting 2024 brought media industry experts together for three days in New York City to discuss many topics including AI, archives and authenticity.
Hosted by both The New York Times and Associated Press, over 50 attendees from 14 countries participated in person, with another 30+ delegates attending online.
As usual, the IPTC Working Group leads presented a summary of their most recent work, including a new release of NewsML-G2 (version 2.34, which will be released very soon); forthcoming work on ninjs to support events, planned news coverage and live streamed video; updates to NewsCodes vocabularies; more evangelism of IPTC Sport Schema; and further work on Video Metadata Hub, the IPTC Photo Metadata Standard and our emerging framework for a simple way to express common rights statements using RightsML.
We were very happy to hear many IPTC member organisations presenting at the Spring Meeting. We heard from:
- Anna Dickson of recently-joined member Google talked about their work with IPTC in the past and discussed areas where we could collaborate in the future
- Aimee Rinehart of Associated Press presented AP’s recent report on the use of generative AI in local news
- Scott Yates of JournalList gave an update on the trust.txt protocol
- Andreas Mauczka, Chief Digital Officer at Austria Press Agency APA presented on APA’s framework for use of generative AI in their newsroom
- Drew Wanczowski of Progress Software gave a demonstration of how IPTC standards can be implemented in Progress’s tools such as Semaphore and MarkLogic
- Vincent Nibart and Geert Meulenbelt of new IPTC Startup Member Kairntech presented on their recent work with AFP on news categorisation using IPTC Media Topics and other vocabularies
- Mathieu Desoubeaux of IPTC Startup Member IMATAG presented their work, also with AFP, on watermarking images for tracking and metadata retrieval purposes
In addition we heard from guest speakers:
- Jim Duran of the Vanderbilt TV News Archive spoke about how they are using AI to catalog and tag their extensive archive of decades of broadcast news content
- John Levitt of Elvex spoke about their system which allows media organisations to present a common interface (web interface and developer API) to multiple generative AI models, including tracking, logging, cost monitoring, permissions and other governance features which are important to large organisations using AI models.
- Toshit Panigrahi, co-founder of TollBit spoke about their platform for “AI content licensing at scale”, allowing content owners to establish rules and monitoring around how their content should be licensed for both the training of AI models and for retrieval-augmented generation (RAG)-style on-demand content access by AI agents.
- We also heard an update about the TEMS – Trusted European Media Data Space project.
 We were also lucky enough to take tours of the Associated Press Corporate Archive on Tuesday and the New York Times archive on Wednesday. Valierie Komor of AP Corporate Archives and Jeff Roth of The New York Times Archival Library (known to staffers as “the morgue”) both gave fascinating insights and stories about how both archives preserve the legacy of these historically important news organisations.
We were also lucky enough to take tours of the Associated Press Corporate Archive on Tuesday and the New York Times archive on Wednesday. Valierie Komor of AP Corporate Archives and Jeff Roth of The New York Times Archival Library (known to staffers as “the morgue”) both gave fascinating insights and stories about how both archives preserve the legacy of these historically important news organisations.
Brendan Quinn, speaking for Judy Parnall of the BBC, also presented an update of the recent work of C2PA and Project Origin and introduced the new IPTC Media Provenance Committee, dedicated to bringing C2PA technology to the news and media industry.
On behalf all attendees, we would like to thank The New York Times and Associated Press for hosting us, and especially to thank Jennifer Parrucci of The New York Times and Heather Edwards of The Associated Press for their hard work in coordinating use of their venues for our meeting.
The next IPTC Member Meeting will be the 2024 Autumn Meeting, which will be held online from Monday September 30th to Wednesday October 2nd, and will include the 2024 IPTC Annual General Meeting. The Spring Meeting 2025 will be held in Western Europe at a location still to be determined.
The 2024 IPTC Photo Metadata Conference takes place as a webinar on Tuesday 7th May from 1500 – 1800 UTC. Speakers hail from Adobe (makers of Photoshop), CameraBits (makers of PhotoMechanic), Numbers Protocol, Colorhythm, vAIsual and more.
First off, IPTC Photo Metadata Working Group co-leads, David Riecks and Michael Steidl, will give an overview of what has been happening in the world of photo metadata since our last Conference in November 2022, including IPTC’s work on metadata for AI labelling, “do not train” signals, provenance, diversity and accessibility.
Next, a panel session on AI and Image Authenticity: Bringing trust back to photography? discusses approaches to the problem of verifying trust and credibility for online images. The panel features C2PA lead architect Leonard Rosenthol (Adobe), Dennis Walker (Camera Bits), Neal Krawetz (FotoForensics) and Bofu Chen (Numbers Protocol).
Next, James Lockman of Adobe presents the Custom Metadata Panel, which is a plugin for Photoshop, Premiere Pro and Bridge that allows for any XMP-based metadata schema to be used – including IPTC Photo Metadata and IPTC Video Metadata Hub. James will give a demo and talk about future ideas for the tool.
Finally, a panel on AI-Powered Asset Management: Where does metadata fit in? discusses teh relevance of metadata in digital asset management systems in an age of AI. Speakers include Nancy Wolff (Cowan, DeBaets, Abrahams & Sheppard, LLP), Serguei Fomine (IQPlug), Jeff Nova (Colorhythm) and Mark Milstein (vAIsual).
The full agenda and links to register for the event are available at https://iptc.org/events/photo-metadata-conference-2024/
Registration is free and open to anyone who is interested.
See you there on Tuesday 7th May!
The IPTC Photo Metadata Working Group has updated the IPTC Photo Metadata User Guide, including guidance for accessibility and for tagging AI-generated images with metadata.
The updates to the User Guide are across several areas:
- A guide to using the accessibility fields added in IPTC Photo Metadata Standard version 2021.1 (Alt Text (Accessibility) and Extended Description (Accessibility) has been added
-
A new section with guidance for applying metadata to AI-generated images has been added
-
Guides for new fields added: Event Identifier, Product/Identifier, Contributor, Data Mining
-
The Metadata Usage Examples section has been updated to reflect some of the recently-added fields
-
The guidance on fields and topics has generally been reviewed and updated
Please let us know if you spot any other areas of the user guide that should be updated or if you have suggestions for more guidance that we could give.
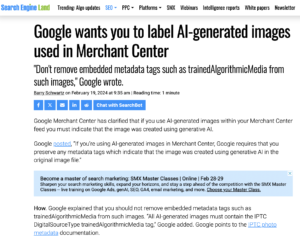
Google has added Digital Source Type support to Google Merchant Center, enabling images created by generative AI engines to be flagged as such in Google’s products such as Google search, maps, YouTube and Google Shopping.
In a new support post, Google reminds merchants who wish their products to be listed in Google search results and other products that they should not strip embedded metadata, particularly the Digital Source Type field which can be used to signal that content was created by generative AI.
We at the IPTC fully endorse this position. We have been saying for years that website publishers should not strip metadata from images. This should also include tools for maintaining online product inventories, such as Magento and WooCommerce. We welcome contact from developers who wish to learn more about how they can preserve metadata in their images.
Here’s the full text of Google’s recommendation:

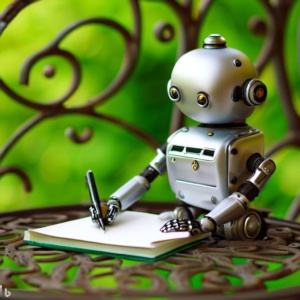
Yesterday Nick Clegg, Meta’s President of Global Affairs, announced that Meta would be using IPTC embedded photo metadata to label AI-Generated Images on Facebook, Instagram and Threads.
Meta already uses the IPTC Photo Metadata Standard’s Digital Source Type property to label images generated by its platform. The image to the right was generated using Imagine with Meta AI, Meta’s image generation tool. Viewing the image’s metadata with the IPTC’s Photo Metadata Viewer tool shows that the Digital Source Type field is set to “trainedAlgorithmicMedia” as recommended in IPTC’s Guidance on metadata for AI-generated images.
Clegg said that “we do several things to make sure people know AI is involved, including putting visible markers that you can see on the images, and both invisible watermarks and metadata embedded within image files. Using both invisible watermarking and metadata in this way improves both the robustness of these invisible markers and helps other platforms identify them.”
This approach of both direct and indirect disclosure is in line with the Partnership on AI’s Best Practices on signalling the use of generative AI.
Also, Meta are building recognition of this metadata into their tools: “We’re building industry-leading tools that can identify invisible markers at scale – specifically, the “AI generated” information in the C2PA and IPTC technical standards – so we can label images from Google, OpenAI, Microsoft, Adobe, Midjourney, and Shutterstock as they implement their plans for adding metadata to images created by their tools.”
We have previously shared the news that Google, Microsoft, Adobe, Midjourney and Shutterstock will use IPTC metadata in their generated images, either directly in the IPTC Photo Metadata block or using the IPTC Digital Source Type vocabulary as part of a C2PA assertion. OpenAI has just announced that they have started using IPTC via C2PA metadata to signal the fact that images from DALL-E are generated by AI.
A call for platforms to stop stripping image metadata
We at the IPTC agree that this is a great step towards end-to-end support of indirect disclosure of AI-generated content.
As the Meta and OpenAI posts points out, it is possible to strip out both IPTC and C2PA metadata either intentionally or accidentally, so this is not a solution to all problems of content credibility.
Currently, one of the main ways metadata is stripped from images is when they are uploaded to Facebook or other social media platforms. So with this step, we hope that Meta’s platforms will stop stripping metadata from images when they are shared – not just the fields about generative AI, but also the fields regarding accessibility (alt text), copyright, creator’s rights and other information embedded in images by their creators.
Video next?
Meta’s post indicates that this type of metadata isn’t commonly used for video or audio files. We agree, but to be ahead of the curve, we have added Digital Source Type support to IPTC Video Metadata Hub so videos can be labelled in the same way.
We will be very happy to work with Meta and other platforms on making sure IPTC’s standards are implemented correctly in images, videos and other areas.

As we wrap up 2023, we thought it would be useful to give an update you on the IPTC’s work in 2023, including updates to most of our standards.
Two successful member meetings, one in person!
This year we finally held our first IPTC Member meeting in person since 2019, in Tallinn Estonia. We had around 30 people attend in person and 50 attended online from over 40 organisations. Presentations and discussions ranged from the e-Estonia digital citizen experience to building re-usable news content widgets with Web Components, and of course included generative AI, credibility and fact checking, and more. Here’s our report on the IPTC 2023 Spring Meeting.
For our Autumn Meeting we went back to an online format, with over 50 attendees, and more watching the recordings afterwards (which are available to all members). Along with discussions of generative AI and content licensing at this year’s meetings, it was great to hear the real-world implementation experience of the ASBU Cloud project from the Arab States Broadcasting Union. The system was created by IPTC members Broadcast Solutions, based on NewsML-G2. The DPP Live Production Exchange, led by new members Arqiva, will be another real-world implementation coming soon. We heard about the project’s first steps at the Autumn Meeting.
Also at this years Autumn Meeting we also heard from Will Kreth of the HAND Identity platform and saw a demo of IPTC Sport Schema from IPTC member Progress Software (previously MarkLogic). More on IPTC Sport Schema below! All news from the Autumn Meeting is summed up in our post AI, Video in the cloud, new standards and more: IPTC Autumn Meeting 2023
We’re very happy to say that the IPTC Spring Meeting 2024 will be held in New York from April 15 – 17. All IPTC member delegates are welcome to attend the meeting at no cost. If you are not a member but would like to present your work at the meeting, please get in touch using our Contact Us form.
IPTC Photo Metadata Conference, 7 May 2024: save the date!
Due to several issues, we were not able to run a Photo Metadata Conference in 2023, but we will be back with an online Photo Metadata Conference on 7th May 2024. Please mark the date in your calendar!
As usual, the event will be free and open for anyone to attend.
If you would like to present to the people most interested in photo metadata from around the world, please let us know!
Presentations at other conferences and work with other organisations
IPTC was represented at the CEPIC Congress in France, the EBU DataTech Seminar in Geneva, Sports Video Group Content Management Forum in New York and the DMLA’s International Digital Media Licensing Conference in San Francisco.
We also worked with CIPA, the organisation behind the Exif photo metadata standard, on aligning Exif with IPTC Photo Metadata, and supported them in their work towards Exif 3.0 which was announced in June.
The IPTC will be advising the TEMS project which is an EU-funded initiative to build a “media data space” for Europe, and possibly beyond: IPTC working with alliance to build a European Media Data Space.
IPTC’s work on Generative AI and media
Of course the big topic for media in 2023 has been Generative AI. We have been looking at this topic for several years, since it was known as “synthetic media” and back in 2022 we created a taxonomy of “digital source types” that can be used to describe various forms of machine-generated and machine-assisted content creation. This was a joint effort across our NewsCodes, Video Metadata and Photo Metadata Working Groups.
It turns out that this was very useful, and the IPTC Digital Source Type taxonomy has been adopted by Google, Midjourney, C2PA and others as a way to describe content. Here are some of our news posts from 2023 on this topic:
- IPTC publishes metadata guidance for AI-generated “synthetic media”
- Google announces use of IPTC metadata for generative AI images
- Midjourney and Shutterstock AI sign up to use of IPTC Digital Source Type to signal generated AI content
- Microsoft announces signalling of generative AI content using IPTC and C2PA metadata
- Royal Society/BBC workshop on Generative AI and content provenance
- New “digital source type” term added to support inpainting and outpainting in Generative AI
- IPTC releases technical guidance for creating and editing metadata, including DigitalSourceType
IPTC’s work on Trust and Credibility

After a lot of drafting work over several years, we released the Guidelines for Expressing Trust and Credibility signals in IPTC standards that shows how to embed trust infiormation in the form of “trust indicators” such as those from The Trust Project into content marked up using IPTC standards such as NewsML-G2 and ninjs. The guideline also discusses how media can be signed using C2PA specification.
We continue to work with C2PA on the underlying specification allowing signed metadata to be added to media content so that it becomes “tamper-evident”. However C2PA specification in its current form does not prescribe where the certificates used for signing should come from. To that end, we have been working with Microsoft, BBC, CBC / Radio Canada and The New York Times on the Steering Committee of Project Origin to create a trust ecosystem for the media industry. Stay tuned for more developments from Project Origin during 2024.
IPTC’s newest standard: IPTC Sport Schema
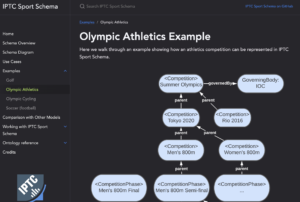
After years of work, the IPTC Sports Content Working Group released version 1.0 of IPTC Sport Schema. IPTC Sport Schema takes the experience of IPTC’s 10+ years of maintaining the XML-based SportsML standard and applies it to the world of the semantic web, knowledge graphs and linked data.
Paul Kelly, Lead of the IPTC Sports Content Working Group, presented IPTC Sport Schema to the world’s top sports media technologists: IPTC Sport Schema launched at Sports Video Group Content Management Forum.
Take a look at out dedicated site https://sportschema.org/ to see how it works, look at some demonstration data and try out a query engine to explore the data.
If you’re interested in using IPTC Sport Schema as the basis for sports data at your organisation, please let us know. We would be very happy to help you to get started.
Standard and Working Group updates
- Our IPTC NewsCodes vocabularies had two big updates, the NewsCodes 2023-Q1 update and the NewsCodes Q3 2023 update. For our main subject taxonomy Media Topics, over the year we added 12 new concepts, retired 73 under-used terms, and modified 158 terms to make their labels and/or descriptions easier to understand. We also added or updated vocabularies such as Digital Source Type and Authority Status.
- The News in JSON Working Group released ninjs 2.1 and ninjs 1.5 in parallel, so that people who cannot move from the 1.x schema can still get the benefits of new additions. The group is currently working on adding events and planning items to ninjs based on requirements the DPP Live Production Exchange project: expect to see something released in 2024.
- NewsML-G2 2.32 and NewsML-G2 v2.33 were released this year, including support for Generative AI via the Digital Source Type vocabulary.
- The IPTC Photo Metadata Standard 2023.1 allows rightsholders to express whether or not they are willing to allow their content to be indexed by search engines and data mining crawlers, and whether the content can be used as training data for Generative AI. This work was done in partnership with the PLUS Coalition. We also updated the IPTC Photo Metadata Mapping Guidelines to accommodate Exif 3.0.
- Through discussions and workshops at our Member Meetings in 2022 and 2023, we have been working on making RightsML easier to use and easier to understand. Stay tuned for more news on RightsML in 2024.
- Video Metadata Hub 1.5 adds the same properties to allow content to be excluded from generative AI training data sets. We have also updated the Video Metadata Hub Generator tool to generate C2PA-compliant metadata “assertions”.
New faces at IPTC
Ian Young of Alamy / PA Media Group stepped up to become the lead of the News in JSON Working Group, taking over from Johan Lindgren of TT who is winding down his duties but still contributes to the group.
We welcomed Bonnier News, Newsbridge, Arqiva, the Australian Broadcasting Corporation and Neuwo.ai as new IPTC members, plus a very well known name who will be joining at the start of 2024. We’re very happy to have you all as members!
We are always happy to work with more organisations in the media and related industries. If you would like to talk to us about joining IPTC, please complete our membership enquiry form.
Here’s to a great 2024!
Thanks to everyone who gave IPTC your support, and we look forward to working with you in the coming year.
If you have any questions or comments (and especially if you would like to speak at one of our events in 2024!), you can contact us via our contact form.
Best wishes,
Brendan Quinn
Managing Director, IPTC
and the IPTC Board of Directors: Dave Compton (LSE Group), Heather Edwards (The Associated Press), Paul Harman (Bloomberg LP), Gerald Innerwinkler (APA), Philippe Mougin (Agence France-Presse), Jennifer Parrucci (The New York Times), Robert Schmidt-Nia of DATAGROUP (Chair of the Board), Guowei Wu (Xinhua)
 The IPTC is happy to announce the latest version of our guidance for mapping between photo metadata standards.
The IPTC is happy to announce the latest version of our guidance for mapping between photo metadata standards.
Following our publication of IPTC’s rules for mapping photo metadata between IPTC, Exif and schema.org standards in 2022, the IPTC Photo Metadata Working Group has been monitoring updates in the photo metadata world.
In particular, the IPTC gave support and advice to CIPA while it was working on Exif 3.0 and we have updated our mapping rules to work with the latest changes to Exif expressed in Exif 3.0.
As well as guidelines for individual properties between IPTC Photo Metadata Standard (in both the older IIM form and the newer XMP embedding format), Exif and schema.org, we have included some notes on particular considerations for mapping contributor, copyright notice, dates and IDs.
The IPTC encourages all developers who previously consulted the out-of-date Metadata Working Group guidelines (which haven’t been updated since 2008 and are no longer published) to use this guide instead.

Updated in June 2024 to include an image containing the new metadata property
Many image rights owners noticed that their assets were being used as training data for generative AI image creators, and asked the IPTC for a way to express that such use is prohibited. The new version 2023.1 of the IPTC Photo Metadata Standard now provides means to do this: a field named “Data Mining” and a standardised list of values, adopted from the PLUS Coalition. These values can show that data mining is prohibited or allowed either in general, for AI or Machine Learning purposes or for generative AI/ML purposes. The standard was approved by IPTC members on 4th October 2023 and the specifications are now publicly available.
Because these data fields, like all IPTC Photo Metadata, are embedded in the file itself, the information will be retained even after an image is moved from one place to another, for example by syndicating an image or moving an image through a Digital Asset Management system or Content Management System used to publish a website. (Of course, this requires that the embedded metadata is not stripped out by such tools.)
Created in a close collaboration with PLUS Coalition, the publication of the new properties comes after the conclusion of a public draft review period earlier this year. The properties are defined as part of the PLUS schema and incorporated into the IPTC Photo Metadata Standard in the same way that other properties such as Copyright Owner have been specified.
The new properties are now finalised and published. Specifically, the new properties are as follows:
- Data Mining: a field with a value from a controlled value vocabulary. Values come from the PLUS Data Mining vocabulary, reproduced here:
- http://ns.useplus.org/ldf/vocab/DMI-UNSPECIFIED (Unspecified – no prohibition defined)
- http://ns.useplus.org/ldf/vocab/DMI-ALLOWED (Allowed)
- http://ns.useplus.org/ldf/vocab/DMI-PROHIBITED-AIMLTRAINING (Prohibited for AI/ML training)
- http://ns.useplus.org/ldf/vocab/DMI-PROHIBITED-GENAIMLTRAINING (Prohibited for Generative AI/ML training)
- http://ns.useplus.org/ldf/vocab/DMI-PROHIBITED-EXCEPTSEARCHENGINEINDEXING (Prohibited except for search engine indexing)
- http://ns.useplus.org/ldf/vocab/DMI-PROHIBITED (Prohibited)
- http://ns.useplus.org/ldf/vocab/DMI-PROHIBITED-SEECONSTRAINT (Prohibited, see Other Constraints property)
- http://ns.useplus.org/ldf/vocab/DMI-PROHIBITED-SEEEMBEDDEDRIGHTSEXPR (Prohibited, see Embedded Encoded Rights Expression property)
- http://ns.useplus.org/ldf/vocab/DMI-PROHIBITED-SEELINKEDRIGHTSEXPR (Prohibited, see Linked Encoded Rights Expression property)
- Other Constraints: Also defined in the PLUS specification, this text property is to be used when the Data Mining property has the value “http://ns.useplus.org/ldf/vocab/DMI-PROHIBITED-SEECONSTRAINT“. It can specify, in a human-readable form, what other constraints may need to be followed to allow Data Mining, such as “Generative AI training is only allowed for academic purposes” etc.
The IPTC and PLUS Consortium wish to draw users attention to the following notice included in the specification:
Regional laws applying to an asset may prohibit, constrain, or allow data mining for certain purposes (such as search indexing or research), and may overrule the value selected for this property. Similarly, the absence of a prohibition does not indicate that the asset owner grants permission for data mining or any other use of an asset.
The prohibition “Prohibited except for search engine indexing” only permits data mining by search engines available to the public to identify the URL for an asset and its associated data (for the purpose of assisting the public in navigating to the URL for the asset), and prohibits all other uses, such as AI/ML training.
The IPTC encourages all photo metadata software vendors to incorporate the new properties into their tools as soon as possible, to support the needs of the photo industry.
ExifTool, the command-line tool for accessing and manipulating metadata in image files, already supports the new properties. Support was added in the ExifTool version 12.67 release, which is available for download on exiftool.org.
The new version of the specification can be accessed at https://www.iptc.org/std/photometadata/specification/IPTC-PhotoMetadata or from the navigation menu on iptc.org. The IPTC Get Photo Metadata tool and IPTC Photo Metadata Reference images been updated to use the new properties.
The IPTC and PLUS Coalition wish to thank many IPTC and PLUS member organisations and others who took part in the consultation process around these changes. For further information, please contact IPTC using the Contact Us form.

![Preserving metadata tags for AI-generated images in Merchant Center
February 2024
If you’re using AI-generated images in Merchant Center, Google requires that you preserve any metadata tags which indicate that the image was created using generative AI in the original image file.
Don't remove embedded metadata tags such as trainedAlgorithmicMedia from such images. All AI-generated images must contain the IPTC DigitalSourceType trainedAlgorithmicMedia tag. Learn more about IPTC photo metadata.
These requirements apply to the following image attributes in Merchant Center Classic and Merchant Center Next:
Image link [image_link]
Additional image link [additional_image_link]
Lifestyle image link [lifestyle_image_link]
Learn more about product data specifications.](https://iptc.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/Screenshot-2024-02-20-at-09.56.52-1024x724.png)