Categories
Archives
 On Tuesday 12 November 2023, a group of news, journalism and media organisations released what they call the “Paris Charter on AI and Journalism.” Created by 17 organisations brought together by Reporters sans frontières and chaired by journalist and Nobel Peace Prize laureate Maria Ressa, the Charter aims to give journalism organisations some guidelines that they can use to navigate the intersection of Artificial Intelligence systems and journalism.
On Tuesday 12 November 2023, a group of news, journalism and media organisations released what they call the “Paris Charter on AI and Journalism.” Created by 17 organisations brought together by Reporters sans frontières and chaired by journalist and Nobel Peace Prize laureate Maria Ressa, the Charter aims to give journalism organisations some guidelines that they can use to navigate the intersection of Artificial Intelligence systems and journalism.
The IPTC particularly welcomes the Charter because it aligns well with several of our ongoing initiatives and recent projects. IPTC technologies and standards give news organisations a way to implement the Charter simply and easily in their existing newsroom workflows.
In particular, we have some comments to offer on some principles:
Principle 3: AI SYSTEMS USED IN JOURNALISM UNDERGO PRIOR, INDEPENDENT EVALUATION
“The AI systems used by the media and journalists should undergo an independent, comprehensive, and thorough evaluation involving journalism support groups. This evaluation must robustly demonstrate adherence to the core values of journalistic ethics. These systems must respect privacy, intellectual property and data protection laws.”
We particularly agree that AI systems must respect intellectual property laws. To support this, we have recently released the Data Mining property in the IPTC Photo Metadata Standard which allows content owners to express any permissions or restrictions that they apply regarding the use of their content in Generative AI training or other data mining purposes. The Data Mining property is also supported in IPTC Video Metadata Hub.
Principle 5: MEDIA OUTLETS MAINTAIN TRANSPARENCY IN THEIR USE OF AI SYSTEMS.
“Any use of AI that has a significant impact on the production or distribution of journalistic content should be clearly disclosed and communicated to everyone receiving information alongside the relevant content. Media outlets should maintain a public record of the AI systems they use and have used, detailing their purposes, scopes, and conditions of use.”
To enable clear declaration of generated content, we have created extra terms in the Digital Source Type vocabulary to express content that was created or edited by AI. These values can be used in both IPTC Photo Metadata and IPTC Video Metadata Hub.
Principle 6: MEDIA OUTLETS ENSURE CONTENT ORIGIN AND TRACEABILITY.
“Media outlets should, whenever possible, use state-of-the-art tools that guarantee the authenticity and provenance of published content, providing reliable details about its origin and any subsequent changes it may have undergone. Any content not meeting these authenticity standards should be regarded as potentially misleading and should undergo thorough verification.”
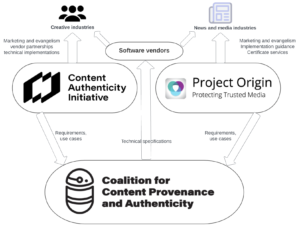
Through IPTC’s work with Project Origin, C2PA and the Content Authenticity Initiative, we are pushing forward in making provenance and authenticity technology available and accessible to journalists and newsrooms around the world.
In conclusion, the Charter says: “In affirming these principles, we uphold the right to information, champion independent journalism, and commit to trustworthy news and media outlets in the era of AI.”
The IPTC is proud to announce that after intense work by most of its Working Groups, we have published version 1.0 of our guidelines document: Expressing Trust and Credibility Information in IPTC Standards.
The culmination of a large amount of work over the past several years across many of IPTC’s Working Groups, the document represents a guide for news providers as to how to express signals of trust known as “Trust Indicators” into their content.
Trust Indicators are ways that news organisations can signal to their readers and viewers that they should be considered as trustworthy publishers of news content. For example, one Trust Indicator is a news outlet’s corrections policy. If the news outlet provides (and follows) a clear guideline regarding when and how it updates its news content.
The IPTC guideline does not define these trust indicators: they were taken from existing work by other groups, mainly the Journalism Trust Initiative (an initiative from Reporters Sans Frontières / Reporters Without Borders) and The Trust Project (a non-profit founded by Sally Lehrman of UC Santa Cruz).
The first part of the guideline document shows how trust indicators created by these standards can be embedded into IPTC-formatted news content, using IPTC’s NewsML-G2 and ninjs standards which are both widely used for storing and distributing news content.
The second part of the IPTC guidelines document describes how cryptographically verifiable metadata can be added to media content. This metadata may express trust indicators but also more traditional metadata such as copyright, licensing, description and accessibility information. This can be achieved using the C2PA specification, which implements the requirements of the news industry via Project Origin and of the wider creative industry via the Content Authenticity Initiative. The IPTC guidelines show how both IPTC Photo Metadata and IPTC Video Metadata Hub metadata can be included in a cryptographically signed “assertion”
We expect these guidelines to evolve as trust and credibility standards and specifications change, particularly in light of recent developments in signalling content created by generative AI engines. We welcome feedback and will be happy to make changes and clarifications based on recommendations.
The IPTC sends its thanks to all IPTC Working Groups that were involved in creating the guidelines, and to all organisations who created the trust indicators and the frameworks upon which this work is based.
Feedback can be shared using the IPTC Contact Us form.

Following the recent announcements of Google’s signalling of generative AI content and Midjourney and Shutterstock the day after, Microsoft has now announced that it will also be signalling the provenance of content created by Microsoft’s generative AI tools such as Bing Image Creator.
Microsoft’s efforts go one step beyond those of Google and Midjourney, because they are adding the image metadata in a way that can be verified using digital certificates. This means that not only is the signal added to the image metadata, but verifiable information is added on who added the metadata and when.
As TechCrunch puts it, “Using cryptographic methods, the capabilities, scheduled to roll out in the coming months, will mark and sign AI-generated content with metadata about the origin of the image or video.”
The system uses the specification created by the Coalition for Content Provenance and Authenticity. a joint project of Project Origin and the Content Authenticity Initiative.
The 1.3 version of the C2PA Specification specifies how a C2PA Action can be used to signal provenance of Generative AI content. This uses the IPTC DigitalSourceType vocabulary – the same vocabulary used by the Google and Midjourney implementations.
This follows IPTC’s guidance on how to use the DigitalSourceType property, published earlier this month.
We’re very happy that we can make public some of the video recordings from the recent IPTC Photo Metadata Conference 2020, held on Tuesday 13 October 2020.
Thanks to all who attended – we had over 200 registrations for the webinar.
The videos are embedded below or can be viewed directly on YouTube by following the link above the embedded video.
Introduction
Brendan Quinn, Managing Director of IPTC, opened the day with an introduction to IPTC and an overview of what was to come (10 minutes):
Michael Steidl, Photo Metadata WG lead on IPTC Photo Metadata
Michael Steidl presented on why we should care about photo metadata in his presentation “About IPTC Photo Metadata” (48 minutes including Q&A)
Google’s Licensable Images features
Francois Spies, a Product Manager for Google Images in Mountain View, presented on the Licensable Images features which they developed in consultation with IPTC this year.
After Francois’ presentation, Matthew O’Such, VP SEO for Getty Images and Marcin Czyzewski, CTO and Picturemaxx joined us to share their views on implementing the changes to IPTC Photo Metadata required to power the Google Licensable Images feature. Then we had a Q&A session including Michael, Francois, Matthew and Marcin.
Unfortunately, Google asked us not to make a recording of their presentation or the panel available. However the resources that Francois shared are all available via our Quick Guide to IPTC Photo Metadata and Google Images.
Andy Parsons on the Content Authenticity Initiative
Next up, Andy Parsons (Adobe) introduced the Content Authenticity Initiative (47 minutes including Q&A and a wrap-up of the day from Brendan Quinn):
Thanks again to all our speakers and panellists for their contributions. We’re already looking forward to next year’s event!
Currently next year’s IPTC Photo Metadata Conference is scheduled to be in late May 2021 in Mallorca, Spain in conjunction with the CEPIC Congress 2021. If that proves impractical then we will host another online event.