Categories
Archives
IPTC’s Python library for creating manipulating and managing NewsML-G2 documents, python-newsmlg2, has reached version 1.0.
The earliest versions of the library were created back in 2021, but the code has seen significant changes over that period and we are happy to endorse the latest version as a production-ready 1.0 release.
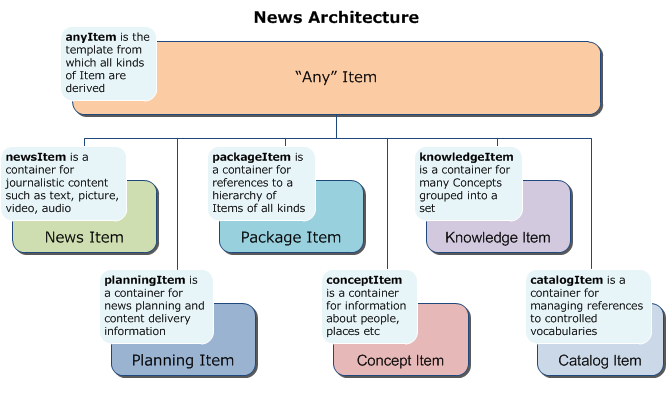
Created as free, open source library that can be integrated into any Python code, the library supports all parts of the NewsML-G2 specification:
- multi-media news stories (NewsItem)
- packages of news content (PackageItem)
- planned news coverage and information about upcoming and past events (PlanningItem and EventsML-G2)
- news content classification concepts and sets of concepts (knowledge graphs) (ConceptItem, KnowledgeItem and CatalogItem)
- syndicated news content transactions (NewsMessage)
The 1.0 version has 98% unit test coverage, which can give users confidence that future changes will not introduce regression bugs.
The code can also handle non-NewsML-G2 content embedded within NewsML-G2 files using XML Schema’s “xs:any” construct. This is a feature of NewsML-G2 that allows any type of markup, such as but not limited to XHTML, NITF or RightsML, to be carried as the payload in a NewsML-G2 NewsItem. The 1.0 version adds “round-trip” support of all xs:any constructs allowing additional markup to be captured, retained and output verbatim, without any loss of fidelity.
The library’s documentation also gives examples of how the library can be used to create, process, manipulate and output NewsML-G2 documents.
The code offers some “helper functions” that make working with NewsML-G2 easier, such as:
- Automatic resolution between QCodes and URIs, two equivalent formats for controlled vocabulary terms, that can now be used interchangeably. The code uses NewsML-G2 Catalogs to look up QCode prefixes and resolve them to URI format.
- Automatic handling of repeatable items and traversal of the NewsML-G2 element structure to provide easy access to child elements such as “
digsrctype = newsitem.contentmeta.digitalsourcetype.uri“
The library can be installed by any Python user using PyPI: pip install newsmlg2.
The source code of the library is freely available, licensed under the open-source MIT licence, at https://github.com/iptc/python-newsmlg2.
Feedback on the library is very welcome. Please let us know what you think on the IPTC Contact Us page or the public NewsML-G2 discussion list.

The IPTC Photo Metadata Working Group is proposing a draft set of properties for recording details of images created using generative AI systems. The group presents a draft of these fields for your comments and feedback. After comments are reviewed the group intends to add new properties to a new version of the IPTC Photo Metadata Standard which would be released later in 2025.
Use Cases
The proposals detailed here are intended to address these scenarios, among others:
- How do you know which system/model generated this image? For instance, if you wanted to compare how different systems—or versions of systems—interpret a given prompt, where would you look?
- How can you know what prompt text was entered, or image shared as a starting point? If you want to recreate similar images in the future with the same look, where should that info be stored?
- How can you tell who was involved in the creation of a generative AI image?
Example Scenario
You are the new designer for an organisation, and need to create an image for a monthly column. You are told to use generative AI, but your boss wants the end result to have the same “look and feel” as images used previously in the column. If you needed to find those that were published previously—what information would be most useful in locating and retrieving the image(s) in your organization’s image collection?
Proposed Properties:
- AI Model
Name: AI Model
Definition: The foundational model name and version used to generate this image.
User Note: For example “DALL-E 2”, “Google Genesis 1.5 Pro”
Basic Specs: Data type: Text / Cardinality: 0..1 - AI Text Prompt Description
Name: AI Text Prompt Description
Definition: The information that was given to the generative AI service as “prompt(s)” in order to generate this image.
User Note: This may include negative [excludes] and positive [includes] statements in the prompt.
Basic Specs: Data type: Text / Cardinality: 0..1 - AI Prompt Writer Name
Name: AI Prompt Writer Name
Definition: Name of the person who wrote the prompt used for generating this image.
Basic Specs: Data type: Text / Cardinality: 0..1 - Reference Image(s)
Name: Reference Image
Definition: Image(s) used as a starting point to be refined by the generative AI system (sometimes referred to as “base image”).
Basic Specs: Data type: URI / Cardinality: 0..unbounded
All of these properties are of course optional, not required, but we would recommend that AI engines fill in the properties whenever possible.
Request for Comment
The intent is for a new standard version including these fields to be proposed at the IPTC Autumn Meeting 2025 in October to be voted on by IPTC member organisations. If approved by members, the new version would be published in November 2025.
Please send your comments or suggestions for improvements using the IPTC Contact Us form or via a post to the public iptc-photometadata@groups.io discussion list by Friday 29th August 2025.
The IPTC has released a guide helping news organisations to sign their news content using C2PA technology.
The guidance was launched at today’s Content Authenticity Summit in New York, co-hosted by IPTC along with the Content Authenticity Initiative and the Coalition for Content Provenance and Authenticity (C2PA).
The guide walks publishers and broadcasters through the steps of evaluating and understanding why they should want to implement content provenance at their organisation, and what they aim to achieve. The guide suggests some use cases and reasons that media organisations might want to consider while planning their implementation.
Next, the guide walks through how publishers can obtain a certificate from one of our Certificate Authority partners; submitting the certificate to the Verified News Publisher list, and signing content using your publisher certificate.
The IPTC Media Provenance Committee will adapt the guide over the coming months as the procedure evolves.
For questions on the guidelines or for any other issues regarding the IPTC Origin Verified News Publishers List, please contact IPTC.
The International Press Telecommunications Council (IPTC) is proud to co-host the 2025 Content Authenticity Summit, along with the Coalition for Content Provenance and Authenticity (C2PA) and the Content Authenticity Initiative (CAI). The event will be held tomorrow, Wednesday 4 June at the Cornell University campus on Roosevelt Island, New York City.
The Content Authenticity Summit will convene over 200 of the world’s foremost experts on digital content provenance including implementers, creators, and policymakers for a one-day series of presentations, panels, breakout sessions, and hands-on demonstrations to highlight the latest developments in this essential and fast-moving space.
The Summit, presented by the Content Authenticity Initiative, the Coalition for Content Provenance and Authenticity, and the International Press Telecommunications Council, will highlight current opportunities and challenges focused on driving broad awareness and adoption of Content Credentials.

Brendan Quinn, Managing Director of IPTC, will be hosting two workshops at the Content Authenticity Summit.
Many other IPTC members will also be represented:
- Adobe will have many representatives at the event, including Andy Parsons, Eric Scouten, Pia Blumenthal and Leonard Rosenthol
- Bruce MacCormack of CBC / Radio Canada, Chair of the Media Provenance Committee, will speak about C2PA adoption in the news media
- Helge O. Svela, CEO of Media Cluster Norway will co-host workshops on C2PA in the news industry.
- AFP and IMATAG will present a case study on their project to digitally sign content
- Charlie Halford of the BBC will co-host the workshop on C2PA metadata in the news industry
- Will Kreth of HAND Identity will be speaking about how provenance protects the identities of athletes and entertainers
- Sherif Hanna of Google will be speaking about the forthcoming C2PA Conformance process.
Other speakers include representatives from Meta, LinkedIn, OpenAI, Partnership on AI and Nikon.
We will report on the event later this week. If you’re attending, come and say hello to our members and to IPTC Managing Director Brendan Quinn.

The IPTC has released a set of guidelines expressing best practices that publishers can follow to express the fact that they reserve data-mining rights on their copyrighted content.
All of the recommended techniques use currently available technologies. While the IPTC is advocating both for better acknowledgement in law of current techniques and for clearer, more stable and more scalable techniques for expressing data-mining opt-out, it is important to remember that opt-out can be expressed today, and that publishers shouldn’t wait for future standards to emerge if they want to control data mining rights on their copyrighted content.
Summary of the recommendations
For full detail, please view the PDF opt-out best practices guidelines. A summary of the guidance is provided below.
-
Display a plain-language, visible rights reservation declaration for all copyrighted content
To ensure no misrepresentation, ensure that copyright and rights reservations are plainly displayed to human readers. -
Display a rights reservation declaration in metadata tags on copyrighted content
Using schema.org, the IPTC Photo Metadata Standard and/or IPTC Video Metadata Hub, the same human-readable copyright notice and usage terms should be attached to media content where possible. -
Use Internet firewalls to block AI crawler bots from accessing your content
To ensure that crawlers that ignore robots.txt and other metadata cannot access your content, publishers can employ network-level protection to block crawler bots before they can reach your content. -
Instruct AI crawler bots using their user agent IDs in your robots.txt file
Seemingly the simplest method, this is actually one of the most difficult because each AI system’s crawler user-agent must be blocked separately. -
Implement a site-wide tdmrep.json file instructing bots which areas of the site can be used for Generative AI training
The Text and Data Mining Reservation Protocol can and should be used, in combination with other techniques. -
Use the trust.txt “datatrainingallowed” parameter to declare site-wide data mining restrictions or permissions
The trust.txt specification allows a publisher to declare a single, site-wide data mining reservation with a simple command:datatrainingallowed=no. Sites that already use trust.txt should add this parameter if they want to block their entire site from all AI data training. -
Use the IPTC Photo Metadata Data Mining property on images and video files
Announced previously by the IPTC and developed in collaboration with the PLUS Coalition, the Data Mining property allows asset-level control of data mining preferences. An added benefit is that the opt-out preferences travel along with the content, for example when an image supplied by a picture agency is published by one of their customers. -
Use the CAWG Training and Data Mining Assertion in C2PA-signed images and video files
For C2PA-signed content, a special assertion can be used to indicate data mining preferences. -
Use in-page metadata to declare whether robots can archive or cache page content
HTML meta tags can be used to signal to AI crawlers what should be done with content in web pages. We give specific recommendations in the guidelines. -
Use TDMRep HTML meta tags where appropriate to implement TDM declarations on a per-page basis
The HTML meta tag version of TDMRep can be used to convey rights reservations for individual web pages. -
Send Robots Exclusion Protocol directives in HTTP headers where appropriate
X-Robots-Tag headers to HTTP responses can be used alongside or instead of in-page metadata. -
Use TDMRep HTTP headers where appropriate to implement TDM declarations on a per-URL basis
TDMRep also has an HTTP version, so we recommend that it is used if the top-level tdmrep.json file cannot easily convery asset-level opt-out restrictions.
Feedback and comments welcome
The IPTC welcomes feedback and comments on the guidance. We expect to create further iterations of this document in the future as best practices and opt-out technologies change.
Please use the IPTC Contact Us form to provide feedback or ideas on how we could improve the guidance in the future.
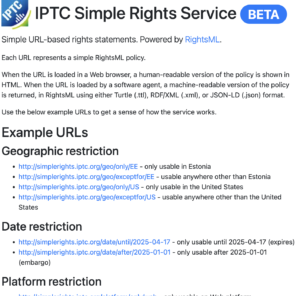
Based on ideas that have arisen at recent conversations and working sessions at IPTC member meetings, we have built a simple service that supports the most common news syndication rights restrictions and permissions. We call it simplerights.iptc.org.
Based on the IPTC’s RightsML standard, which is effectively the same as the W3C’s ODRL, the service allows simple RightsML restrictions to be expressed as simple web URIs (Uniform Resource Indicators). For example, a simple geographic restriction “may be used everywhere except Belgium” can be expressed as https://simplerights.iptc.org/geo/exceptfor/BE.
We have created simple expressions for the following restrictions:
Geographic restriction
- http://simplerights.iptc.org/geo/only/EE – only usable in Estonia
- http://simplerights.iptc.org/geo/exceptfor/EE – usable anywhere other than Estonia
- http://simplerights.iptc.org/geo/only/US – only usable in the United States
- http://simplerights.iptc.org/geo/exceptfor/US – usable anywhere other than the United States
Date restriction
- http://simplerights.iptc.org/date/until/2025-04-17 – only usable until 2025-04-17 (expires)
- http://simplerights.iptc.org/date/after/2025-01-01 – only usable after 2025-01-01 (embargo)
Platform restriction
- http://simplerights.iptc.org/platform/only/web – only usable on Web platform
- http://simplerights.iptc.org/platform/exceptfor/tv – not usable on TV
See Usage Terms restriction
- http://simplerights.iptc.org/seeterms – consumer must consult Usage Terms information to determine rights
If these URLs are accessed over the web, then they return a human-readable web page explaining the restriction.
If the same URLs are accessed by software, then various forms of the ODRL policy are returned. The request can return RDF information in JSON-LD, RDF/XML and Turtle formats, depending on the query parameters or HTTP Accept headers provided in the request. This mechanism is known as HTTP Content Negotiation.
For more complicated RightsML / ODRL constraints, the RightsML Generator that we announced earlier this week may be useful. This tool will allow users to generate rights statements that include more than one restriction at the same time, which is something that the simplerights service cannot currently do.
simplerights.iptc.org is released as a beta service and should not be relied upon in production at this stage. We reserve the right to change the API and URI structure in the final version of the service.
We see this service as potentially a step towards a commercial rights expressions service that is as simple to use as Creative Commons URL-based licences for common, simple use cases.
The simplerights.iptc.org service will be presented at the IPTC Spring Meeting which will be held in Juan les Pins, France from Wednesday to Friday of this week (14-16 May 2025).
We welcome feedback on the usefulness of the service and how we could improve it in the future. Please contact the IPTC via our Contact Form if you have feedback or suggestions.
Brendan Quinn of IPTC presented alongside Leonard Rosenthol of C2PA at the World-Wide Web Consortium (W3C)’s Authentic Web workshop series this week.
This was the second in a series of online workshops run by the W3C in an effort to bring together the various work on trust, provenance, credibility and authenticity. The first part of the Authentic Web workshop was run in March 2025.
Leonard presented C2PA, its motivations and work done so far, including describing how C2PA technology is currently used by platforms such as LinkedIn and TikTok, and by most generative AI tools to signal AI-generated content.
Then Brendan went on to describe how the IPTC’s Media Provenance Committee has established the Verified News Publisher programme, an industry specific “trust list” of media organisations who are using C2PA certificates to sign their published content.
W3C events mostly run in the open, so the session agenda, pre-read material, minutes and even a video recording of the presentation part of the workshop are all available online, even to non-members. As per W3C policy, the discussion portion of the event was not recorded. This allows for more open discussion.
Present at the workshop were representatives of Google Chrome and Mozilla, the W3C’s Technical Architecture Group (TAG), hardware and software vendors, and others with an interest in the idea of implementing content provenance solutions in their tools.
Depending on the outcome of discussions within the group and at further workshops, this work may lead to a physical meeting later this year.
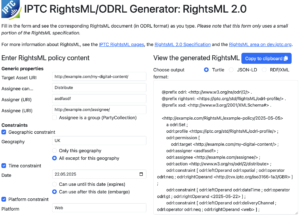
The IPTC has created a RightsML Generator tool that shows how easy it can be to generate simple RightsML documents expressing a range of permissions and obligations around the use of media content.
RightsML is the IPTC’s standard for expressing rights usage statements that can be used for all types of media content, from images and video clips through to AI data, data sets and 3D models. Since version 2.0, RightsML has been based on the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C)‘s Open Digital Rights Language (ODRL); in fact IPTC members worked closely with the W3C to create the current version of ODRL to align with RightsML.
A common complaint among users and potential users of RightsML and ODRL was that it is too complicated to be implemented easily. To answer these issues, we wanted to show that describing rights in RightsML can be relatively simple, especially for common news workflows and rights statements such as:
- “this content may be distributed in all countries except the UK” or “only in the UK” (a common use case for news and image licensing agencies that have operations in one country but allow other agencies to distribute their content in other countries)
- “this content may be published any time after XX date” (a simple “embargo”)
- “this content may be published any time until YY date” (a content expiry notice, which might apply to customers with certain types of licence)
- “this content may be published only on mobile platforms” or “only in print” (based on licensing agreements)
- “this content may be published only to those who have paid a licensing fee”
- or a combination of the above constraints.
To demonstrate these possibilities, we have created a simple form-based tool that generates the relevant RightsML/ODRL document. The user can choose whether to express the RightsML statements in various RDF formats: Turtle, RDF/XML and JSON-LD.
The RightsML generator tool can be accessed at https://iptc.org/std/RightsML/generator/.
Please contact IPTC or post on the public iptc-rightsml discussion group with any feedback or comments. We would love to hear from current and potential users of RightsML to learn how we can make the ecosystem easier for you.
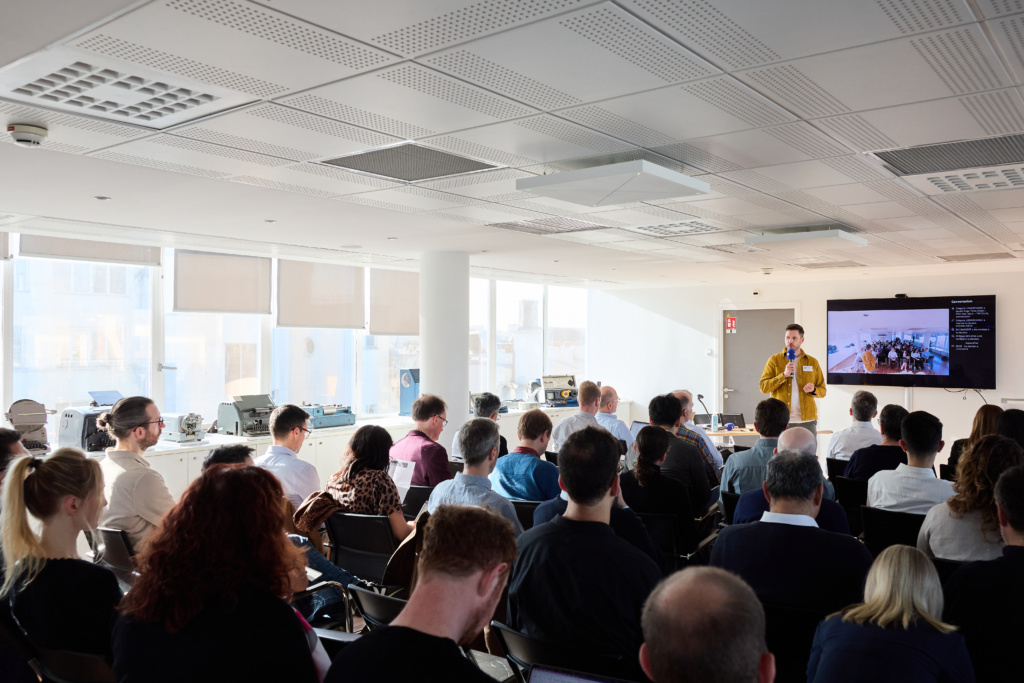

“It has never been more important to safeguard authentic news media,” say the organisers.
“We must strengthen our voice and hold our ground against the big tech players. It is critical that the industry works together,” said Fabrice Fries, Chief Executive Officer at AFP, in his opening remarks for the workshop in Paris.
“At AFP we are committed to ensure that both news organisations and the general public can inspect the provenance of our images. This transparency builds trust,” said Eric Baradat, the global news deputy director for photo and archives at AFP.
AFP, BBC and Media Cluster Norway jointly organised the workshop, which was hosted by AFP and supported by the International Press Telecommunications Council (IPTC). The workshop focused on image metadata and how the C2PA standard, also known as Content Credentials, can safeguard it.
“The challenges the news industry are facing are so great that we can only succeed if we work together. Making sure the public can discern between authentic media and content made by generative AI is vital not only for news organisations, but for democratic societies,” said Helge O. Svela, CEO of Media Cluster Norway.
More than 40 people from over 20 news organisations participated in the full day workshop. Among the presentations was a study commissioned by Media Cluster Norway’s Project Reynir on how media consumers respond to being shown more detailed information about an image. The study was conducted by MediaFutures at the University of Bergen, and built on a user study conducted by the BBC.
“Trust is earned. At the BBC we have seen that users really engage when we show them how their news was made. Extra media provenance details such as when and where an image was taken, or the steps used to verify it, make a real difference to how users trust their news. The C2PA standard can allow us to share this information with the users in a secure and trustworthy way,” said Judy Parnall, Principal Technologist, BBC Research and Development.
Among the participants in the workshop were CBC-Radio Canada, Deutsche Welle, France TV, ITV, NHK and Al Jazeera. Topics discussed included carrying provenance metadata from glass to glass versus adding it at the point of publishing, as well as the importance of redaction to the media industry and content provenance for media archives.
“It is vital that the needs of the news media ecosystem are heard as this technology and standards are further developed and refined,” said Brendan Quinn, Managing Director at IPTC.
The IPTC Media Provenance Committee works on several initiatives for implementing and furthering the development of the C2PA technology for the media industry. Many of the speakers and participants of the Paris workshop are actively involved in this work.
For more information on IPTC and the Media Provenance Committee, contact the IPTC via this site.

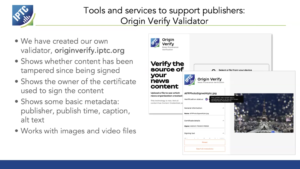
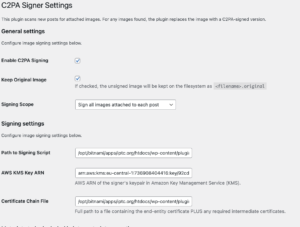
The IPTC has developed a WordPress plugin that automatically signs all images and video content published on a WordPress site. It has been put to use to automatically sign all images attached to IPTC news posts, such as this one, at the moment of publishing.
Based on our library of signing tools which are available to IPTC members, the “C2PA Signer” plugin takes action when a WordPress user publishes a new post. The plugin automatically retrieves all images (in all available sizes) and signs each image using the private key associated with the publisher.
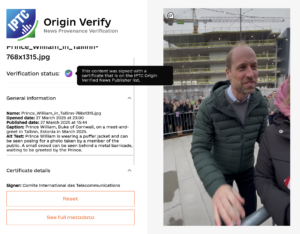
The tool also extracts relevant metadata from WordPress. Each image’s caption, alt text, image upload date and publish date are embedded into the signed C2PA Manifest using an early version of the Origin IPTC Verified News Publisher metadata assertion. The specification of this assertion is currently in flux and the example assertion should not be relied on for production use, although the assertion is supported by the IPTC’s C2PA validator tool, Origin Verify.
Click here to view the image’s signed metadata using the Origin Verify tool.
This is in line with the goals of our IPTC Origin Verified News Publisher project, whereby publishers sign their own content using their own certificate. This enables publishers to take ownership of their content and to assert important facts about their content at the time of publishing.
 |
 |
In related news, the IPTC now has its own C2PA certificate, issued by GlobalSign under the IPTC’s official name, “Comite International des Telecommunications de Presse.” This means that the IPTC can be the first entity to use the new plugin.
“We are very happy to launch the new WordPress plugin, which we of course are using on our own website,” says Brendan Quinn, Managing Director, IPTC. “We believe that this makes us the first organisation to routinely sign all images that we publish using our C2PA credentials.”
The certificates, manifests and the signed content are fully compatible with the latest version of C2PA, version 2.1. Images that we publish (including the image on this post) can be verified using the Origin Verify validator or the C2PA Content Credentials Verify validator.
For more information, contact IPTC using the Contact Us form.
Categories
Archives
- February 2026
- January 2026
- December 2025
- November 2025
- October 2025
- September 2025
- August 2025
- July 2025
- June 2025
- May 2025
- April 2025
- March 2025
- February 2025
- January 2025
- December 2024
- November 2024
- October 2024
- September 2024
- August 2024
- July 2024
- June 2024
- May 2024
- April 2024
- March 2024
- February 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- August 2023
- July 2023
- June 2023
- May 2023
- March 2023
- February 2023
- January 2023
- December 2022
- November 2022
- October 2022
- September 2022
- August 2022
- July 2022
- June 2022
- May 2022
- April 2022
- March 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- December 2021
- November 2021
- October 2021
- September 2021
- August 2021
- July 2021
- June 2021
- May 2021
- April 2021
- February 2021
- December 2020
- November 2020
- October 2020
- September 2020
- August 2020
- July 2020
- June 2020
- May 2020
- April 2020
- March 2020
- February 2020
- December 2019
- November 2019
- October 2019
- September 2019
- July 2019
- June 2019
- May 2019
- April 2019
- February 2019
- November 2018
- October 2018
- September 2018
- August 2018
- July 2018
- June 2018
- May 2018
- April 2018
- March 2018
- January 2018
- November 2017
- October 2017
- September 2017
- August 2017
- June 2017
- May 2017
- April 2017
- December 2016
- November 2016
- October 2016
- September 2016
- August 2016
- July 2016
- June 2016
- May 2016
- April 2016
- February 2016
- January 2016
- December 2015
- November 2015
- October 2015
- September 2015
- June 2015
- April 2015
- March 2015
- February 2015
- November 2014

