Categories
Archives
Following many change requests submitted by news organisations all over the world, the IPTC News in JSON Working Group is happy to announce the 1.2 version of its standard ninjs.
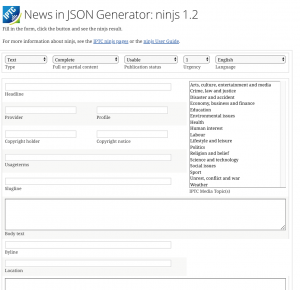
The JSON Schema of the new version can be accessed at https://www.iptc.org/std/ninjs/.
We also created a ninjs User Guide that will enable new and existing users to understand how to put ninjs to use at their organisation.
Version 1.2 is backwards-compatible with version 1.0 and 1.1 and makes no breaking changes.
It includes the following new properties and structures:
- The
firstcreatedproperty goes along with theversioncreatedproperty to specify the date/time when the first version of a news item was published. - The
charcountandwordcountproperties allow the publisher to specify the total character count and word count of a news item (excluding figure captions and metadata). - The
slugline, property allows the publisher to specify a “slug”, a human-readable identifier for the item. (note that no conditions are placed on the usage of this property, usage is up to each publisher). - The
ednote, property allows publishers to specify instructions to editors. - The
infosourcestructure can specify one or many information sources for the news item. It is a metadata structure that can handle literal strings or values from a controlled vocabulary. - The
titleproperty handles “A short natural-language name for the item.”
Also the following sub-properties were added:
- The value
componentwas added to the allowed values fortypeto specify parts of a larger news item. - The description of the
renditionsproperty was changed to allow for any type of rendition, not just images, and new sub-propertiesdurationandformatwere added to enable audio and video renditions (for example, an audio version of a text story).
We have also included a test and validation suite so new versions of the JSON Schema can automatically be checked for compliance and backwards compatibility.
ninjs 1.2 is now included in the SchemaStore.org JSON Schema repository, to aid with editing and validation of ninjs 1.2 files in a range of popular code editors such as Visual Studio Code and Visual Studio 2013+, IntelliJ IDEA, PyCharm and PHPStorm.
For more information, please see:
- The ninjs GitHub repository
- ninjs example documents
- The ninjs User Guide
- The ninjs 1.2 JSON Schema specification
- A new interactive tool for creating example ninjs documents – the ninjs Generator
If you have any questions or comments, please contact the News in JSON Working Group via the public ninjs discussion group, or contact IPTC via the Contact Us form.
IPTC is pleased to release a new version of its widely used Photo Metadata Standard, version 2019.1. This version introduces the exciting new feature to mark regions within an image using embedded metadata, directly in the image file.
Any existing or future IPTC Photo Metadata field can now be attached either to the image as a whole, or to an IPTC Image Region defined within the image.
“IPTC has received many requests from photographers and photo businesses for enabling them to set a region inside an image and to apply specific metadata to it, with the new version of the standard this can be done,” said Michael Steidl, Lead of the IPTC Photo Metadata Working Group. “We hope IPTC Image Regions will be supported by imaging software soon.”
What can IPTC Image Regions be used for?
IPTC Image Regions can be used for many purposes:
- An IPTC Image Region can be used to recommending an area of particular interest in an image to be retained after cropping.
- A photographer or picture editor can use IPTC Image Regions to specify the area to be used if a crop of a different shape is required, such as a square cropping in a landscape shot.
- An IPTC Image Region can frame people in an image, using associated metadata from other fields in the standard attached to only that region, such as Person Shown. This opens up the possibility of news stories avoiding tired “from left to right: Jo Smith, Bill Jones, Susan Bloggs…” image captions. Now we have the ability to embed the names and details of people directly on the region relating to that person, so tools could display people’s names when a user’s pointer hovers over their faces.
- IPTC Image Regions can be used to highlight products, artworks, or locations depicted within an image.
- Another attractive feature of image regions is to identify the copyright owners of multiple photos integrated into a single composite image.
- AI systems identifying objects, text, products and people in images no longer have to include the region information in sidecar files distributed with images. Using IPTC Image Regions, the information can be embedded within the image file itself.
There are many more possible use cases. We are looking forward to seeing applications of IPTC Image Regions that we haven’t even thought of!
What shapes are supported?
According to the Specification, an IPTC Image Region can take the shape of a rectangle, a circle or for more complicated shapes, a polygon with any number of vertices may be used.
Dimensions of image regions can be specified in absolute (pixels) or relative (percentage) formats, and the Specification describes how software should retain IPTC Image Region information so that it is still meaningful after the image is cropped or transformed.
Image types and roles
To help with depicting different types of information using IPTC Image Regions, we have created two fields: Image Region Type and Image Region Role.
- Image Region Type asserts the type of content of the region, denoting whether the image region shows a person, animal, bar code, product etc.
- Image Region Role asserts what the region is used for. Examples might be to specify a recommended cropping area, a sub-image inside a composite image, the main subject to be used for cropping and focus purposes, or a region with special copyright information.
We have created controlled vocabularies that can optionally be used to populate both of these fields and we maintain them as part of the IPTC NewsCodes: Image Region Type and Image Region Role. The IPTC NewsCodes Working Group and Photo Metadata Working Groups may add terms to these vocabularies over time.
What metadata can be added to an IPTC Image Region?
In addition to Image Region Type and Role, any of the existing IPTC Photo Metadata fields can be used to describe an IPTC Image Region. Examples of fields that may be useful to attach to a region are:
- Persons Shown (for name only)
- Person Shown with Details (which supports name and also identifier such as a Wikidata or IMDB ID, controlled vocabulary entries and description)
- Organisations Featured
- Product Shown
- Artwork or Object Shown
- Location Shown (for example, a photograph of a mountain range taken from a distance)
This well organised structure of information about a region in an image can also help software makers to show the boundary of regions and associated metadata at the click of a button.
Help for users and for implementers
Users interested in exploring how IPTC Image Regions can be used can find more in a section about it in the IPTC Photo Metadata User Guide. Some examples are already available showing how an image with regions looks and how they can depict different types of information.
For implementers wanting to support IPTC Image Regions in their software tools, all definitions of the Image Region can be found in the IPTC Photo Metadata Standard specification document. The Specification includes detailed information show to express an image boundary correctly and how to include deliberately used metadata fields describing the content of a region.
Software support
Thanks to Phil Harvey, exiftool has supported IPTC Image Regions since version 11.74. The full source plus Windows and Mac OS packages can be downloaded from https://exiftool.org/.The CPAN version of exiftool does not yet support IPTC Image Regions.
We will link to other software supporting IPTC Image Regions as they become available.
Interested in more information?
- The full specification for IPTC Photo Metadata Standard 2019.1 including IPTC Image regions is available from https://www.iptc.org/std/photometadata/specification/IPTC-PhotoMetadata
- A more user-friendly Photo Metadata User Guidelines can be accessed at https://www.iptc.org/std/photometadata/documentation/userguide/
- See a demo using some example files with marked regions at https://www.iptc.org/std/photometadata/examples/image-region-examples/
- The controlled vocabularies for Image Region Type and Image Region Role can be accessed as part of the IPTC NewsCodes.
Questions, comments, ideas?
We welcome your ideas, thoughts and especially implementations!
Please get in touch via the contact form on this site.
At the IPTC Meeting in Ljubljana Slovenia in Autumn 2019, we welcomed several new faces to IPTC working groups, the Board and voted in a new Chair!
With so many changes happening at the same time, we thought it would be good to introduce the new faces here so members and others can get to know them all better. (All IPTC working group leads, committee leads and directors can be found on the Work Structure and About IPTC pages.)
Video Metadata Working Group lead: Pam Fisher
 Pam Fisher is with IPTC as an Individual Member, and we are very happy to have her lead the Video Metadata Working Group, looking at further development and promotion of Video Metadata Hub and video technology in general.
Pam Fisher is with IPTC as an Individual Member, and we are very happy to have her lead the Video Metadata Working Group, looking at further development and promotion of Video Metadata Hub and video technology in general.
Pam has a long history with media and video technology, working with organisations such as BAFTA, Moving Image Research and Communication Arts.
News in JSON Working Group lead: Johan Lindgren
 Johan has led the Sports Content Working Group since 2016 but with the current resurgence of interest in JSON news formats, decided to move to lead the News in JSON Working Group.
Johan has led the Sports Content Working Group since 2016 but with the current resurgence of interest in JSON news formats, decided to move to lead the News in JSON Working Group.
Representing TT Nyhetsbyrån, Sweden’s national news agency, Johan has been active with IPTC for over 20 years, a regular meeting attendee and has been on the IPTC Board since 2016.
Sports Content Working Group lead: Paul Kelly
With Johan taking the reins of the News in JSON group, Paul is stepping (back) up to lead the Sports Content working group. Paul is also a long-time IPTC member, having been lead of the Sports Content working group from 2005 through to 2016 while he represented XML Team Solutions. Now an independent consultant, Paul has retained his ties with IPTC as an Individual Member and we are very happy to see him leading the Sports Content working group once more.
Chair of the IPTC PR Committee: Linda Burman
Linda has been an Individual Member since 2015, and has actively participated in several working groups including the Photo Metadata and Video Metadata Working Groups. We look forward to reviving the IPTC Public Relations Committee under Linda, looking at how to spread the word about the benefits of IPTC to the media industry and beyond.
New Board member: Jennifer Parrucci
 Jennifer has been an IPTC delegate for the New York Times since 2015, and lead of the News Codes Working Group since 2016. Jennifer has done a great job in leading the News Codes Working Group to maintain and develop the News Codes taxonomies, particularly the Media Topics subject vocabulary. We are looking forward to Jennifer’s contributions to the future of IPTC as part of the Board.
Jennifer has been an IPTC delegate for the New York Times since 2015, and lead of the News Codes Working Group since 2016. Jennifer has done a great job in leading the News Codes Working Group to maintain and develop the News Codes taxonomies, particularly the Media Topics subject vocabulary. We are looking forward to Jennifer’s contributions to the future of IPTC as part of the Board.
New Board member: Paul Harman
 Paul Harman has been an IPTC member for over 20 years, first with Press Association and now with Bloomberg LP. Paul worked on NewsML 1, NewsML-G2 and News in JSON (ninjs) while he was an architect with Press Association and carried it on at Bloomberg, his employer since 2014.
Paul Harman has been an IPTC member for over 20 years, first with Press Association and now with Bloomberg LP. Paul worked on NewsML 1, NewsML-G2 and News in JSON (ninjs) while he was an architect with Press Association and carried it on at Bloomberg, his employer since 2014.
Paul is an active member of the News Architecture, News in JSON and News Codes working groups, and we’re very happy to welcome him to the IPTC Board of Directors.
New Chair: Robert Schmidt-Nia
 Robert has been with IPTC since 2007 representing dpa, the German national news agency, where he has been Managing Director of subsidiary dpa mediatechnology since 2013.
Robert has been with IPTC since 2007 representing dpa, the German national news agency, where he has been Managing Director of subsidiary dpa mediatechnology since 2013.
Robert joined the board of IPTC in 2013 and has been a very active participant, so we were very happy to see him voted by the membership to become Chair of the IPTC Board of Directors.
Welcome to everyone and thanks for sharing your time, knowledge and expertise. Your fellow members appreciate it!
Categories
Archives
- February 2026
- January 2026
- December 2025
- November 2025
- October 2025
- September 2025
- August 2025
- July 2025
- June 2025
- May 2025
- April 2025
- March 2025
- February 2025
- January 2025
- December 2024
- November 2024
- October 2024
- September 2024
- August 2024
- July 2024
- June 2024
- May 2024
- April 2024
- March 2024
- February 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- August 2023
- July 2023
- June 2023
- May 2023
- March 2023
- February 2023
- January 2023
- December 2022
- November 2022
- October 2022
- September 2022
- August 2022
- July 2022
- June 2022
- May 2022
- April 2022
- March 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- December 2021
- November 2021
- October 2021
- September 2021
- August 2021
- July 2021
- June 2021
- May 2021
- April 2021
- February 2021
- December 2020
- November 2020
- October 2020
- September 2020
- August 2020
- July 2020
- June 2020
- May 2020
- April 2020
- March 2020
- February 2020
- December 2019
- November 2019
- October 2019
- September 2019
- July 2019
- June 2019
- May 2019
- April 2019
- February 2019
- November 2018
- October 2018
- September 2018
- August 2018
- July 2018
- June 2018
- May 2018
- April 2018
- March 2018
- January 2018
- November 2017
- October 2017
- September 2017
- August 2017
- June 2017
- May 2017
- April 2017
- December 2016
- November 2016
- October 2016
- September 2016
- August 2016
- July 2016
- June 2016
- May 2016
- April 2016
- February 2016
- January 2016
- December 2015
- November 2015
- October 2015
- September 2015
- June 2015
- April 2015
- March 2015
- February 2015
- November 2014